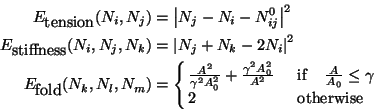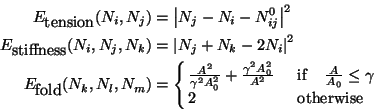Next: Combination Multiquadric Spline (C-MTQ)
Up: Review of Inhomogeneous Registration
Previous: Review of Inhomogeneous Registration
Three-component finite element model (3C-FEM)
[5] gives a finite-element model based on
three tissue types, labelled rigid, deformable and `fluid'. The deformations
are driven by user-supplied landmark displacements and deformations of the
deformable regions are constrained by three energy terms:
where N0ij is the original distance between the nodes Ni and Njand the nodes Ni, Nj and Nk are collinear before deformation; nodes
Nk, Nl and Nm form a triangle with initial area A0 and deformed
area A and 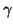 is a threshold of triangular area reduction. The `fluid' deformations are constrained only by
is a threshold of triangular area reduction. The `fluid' deformations are constrained only by
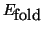 which prevents folding of the image. Rigid regions are obtained by prohibiting the updating of their nodal displacements.
which prevents folding of the image. Rigid regions are obtained by prohibiting the updating of their nodal displacements.
Hava LESTER
1999-03-24