Abstract
Objective It remains unclear whether drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is associated with cumulative brain damage, with no expert consensus and no quantitative syntheses of the available evidence.
Methods We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of MRI studies on progressive atrophy, searching PubMed and Ovid MEDLINE databases for cross-sectional and longitudinal quantitative MRI studies on drug-resistant TLE.
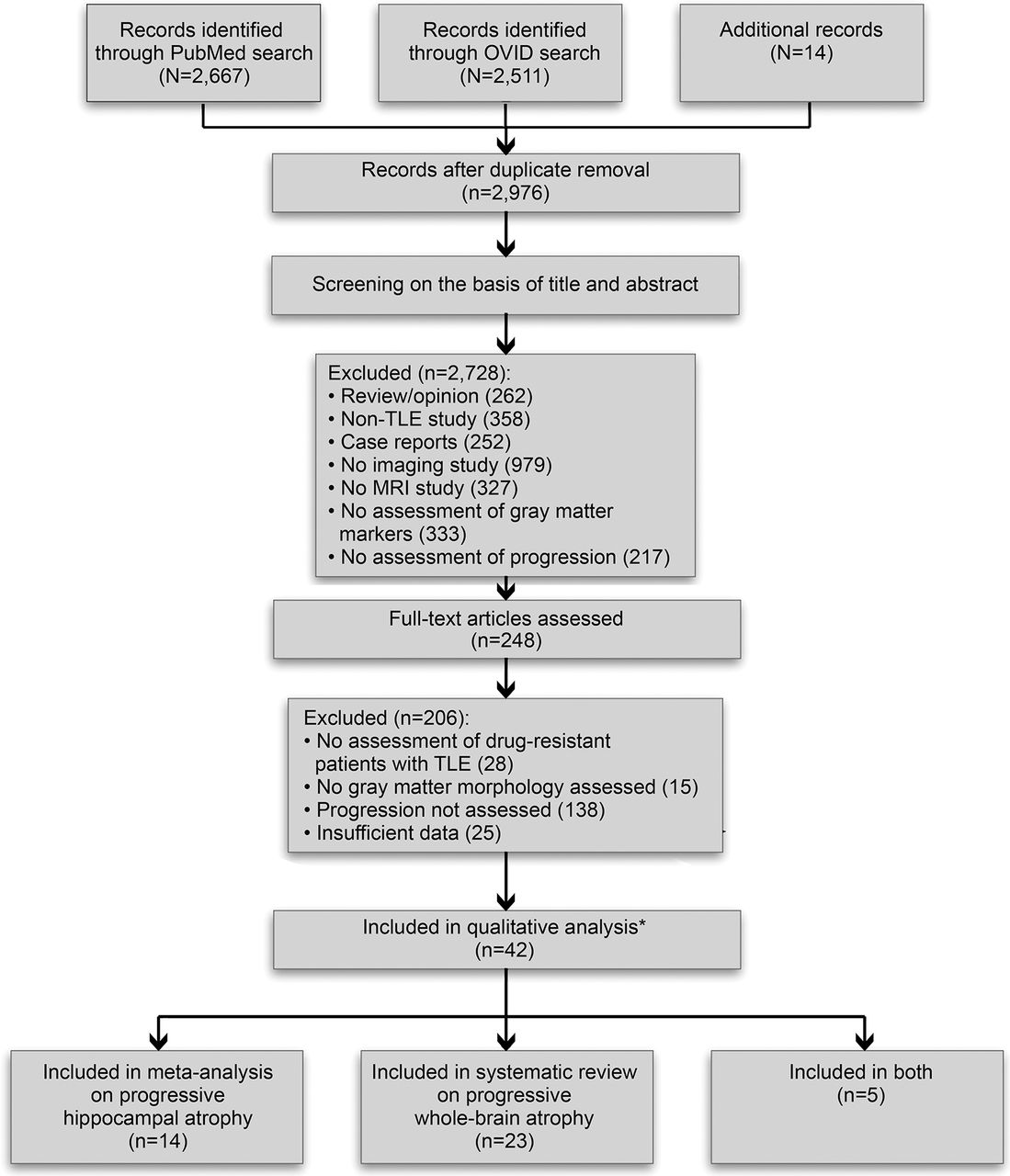
Results We screened 2,976 records and assessed eligibility of 248 full-text articles. Forty-two articles met the inclusion criteria for quantitative evaluation. We observed a predominance of cross-sectional studies, use of different clinical indices of progression, and high heterogeneity in age-control procedures. Meta-analysis of 18/1 cross-sectional/longitudinal studies on hippocampal atrophy (n = 979 patients) yielded a pooled effect size of r = -0.42 for ipsilateral atrophy related to epilepsy duration (95% confidence interval [CI] -0.51 to -0.32; p < 0.0001; I2 = 65.22%) and r = -0.35 related to seizure frequency (95% CI -0.47 to -0.22; p < 0.0001; I2 = 61.97%). Sensitivity analyses did not change the results. Narrative synthesis of 25/3 cross-sectional/longitudinal studies on whole brain atrophy (n = 1,504 patients) indicated that >80% of articles reported duration-related progression in extratemporal cortical and subcortical regions. Detailed analysis of study design features yielded low to moderate levels of evidence for progressive atrophy across studies, mainly due to dominance of cross-sectional over longitudinal investigations, use of diverse measures of seizure estimates, and absence of consistent age control procedures.
Conclusions While the neuroimaging literature is overall suggestive of progressive atrophy in drug-resistant TLE, published studies have employed rather weak designs to directly demonstrate it. Longitudinal multicohort studies are needed to unequivocally differentiate aging from disease progression.